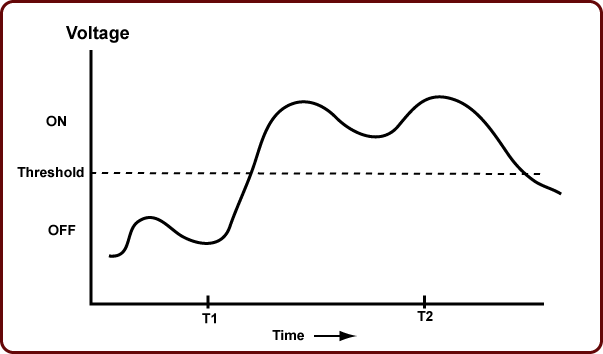
This graph shows an analog signal. When analog systems are used, a threshold is set to determine when the value should be considered ON or OFF.
Analog and Digital systems both have their own advantages and disadvantages, neither one is "better" than the other. An analog signal is one that has a constantly varying state, for example, a circuit where the voltage varies between 0V and 5V. The voltage level, at any given time, could be anywhere between 0 and 5. A digital signal, on the other hand, is binary, that is to say, either on or off.
Analog signals may continuously change in value, and its value can be anything within a set range.

This graph shows an analog signal. When analog systems are used, a threshold is set to determine when the value should be considered ON or OFF.
Digital signals, unlike analog signals, have only two possible states: ON or OFF. Most digital systems use the binary number system to represent the two states, with 0 representing OFF and 1 representing ON. This single on-off value is stored in a bit. A bit is a single on/off value, a 1 or 0. Computers and other electronic devices use binary because it is much easier to replicate the signal 1011 0011 1001 than the analog signal pictures above. Digital systems, because of their binary nature, are much easier to build compared to analog ones.
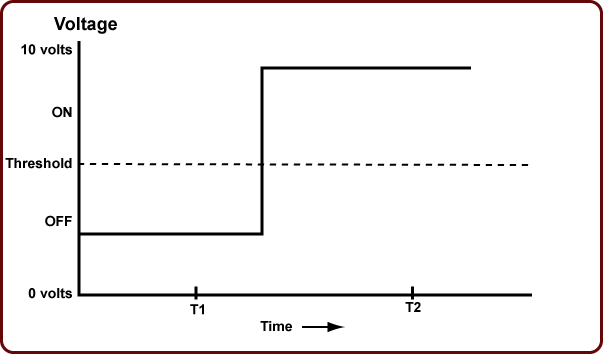
Compare this signal to the one shown above. A digital, or binary signal is either on or off, there is no "in between" value.